2025-03-13
•

Ultrasonic water meters work by using sound waves to measure the flow of water. Ultrasonics involves sound waves of frequencies greater than the upper limit of the audible range for humans—that is, greater than about 20 kilohertz. An ultrasonic transducer is a device used to convert some other type of energy into an ultrasonic vibration. Ultrasonic flow meters work by transmitting ultrasonic waves through the fluid and measuring the time it takes for the waves to travel between transducers.
The difference in transit time between waves traveling with and against the flow is used to calculate the fluid velocity and, consequently, the flow rate.
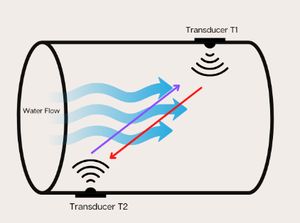
Ultrasonic flow transducer is used as one of the core elements of ultrasonic flow meters. This uses transit time principle, whereby an ultrasonic signal is transmitted from one transducer to another through the f low. Both upstream and downstream measurements are done, and it varies depending on the flow.
When the flow is zero, the time for the signal to get from T1 to T2 is the same as that required to get from T2 to T1. When there is flow, the effect is to boost the speed of the signal in the downstream direction, while decreasing it in the upstream direction. The flowing velocity (Vf) can be determined by the following equation:
Vf =Kdt/TL
Where K is a calibration factor for the volume and time units used, dt is the time differential between upstream and downstream transit times, and TL is the zero-flow transit time. Theoretically, transit-time ultrasonic meters can be very accurate.
Doppler flow meters measure the flow rate of fluids by utilizing the Doppler effect. Doppler effect in physics is defined as the increase (or decrease) in the frequency of waves as the source and observer move towards (or away from) each other. In the context of Doppler flow meters, it refers to the change in frequency of ultrasonic waves as they are reflected off particles or bubbles in the fluid.
There are two ultrasonic transducers, one acting as transmitter and the other as a receiver. The waves sent by the transmitter encounters particles or bubbles suspended in the liquid. These are reflected towards the receiver. If the particles are moving with the fluid flow, the reflected waves experience a change in frequency proportional to the velocity of the fluid. By analysing this shift with respect to the transmitted frequency, the meter determines the velocity of the fluid. This can then be used to calculate the volumetric flow rate.
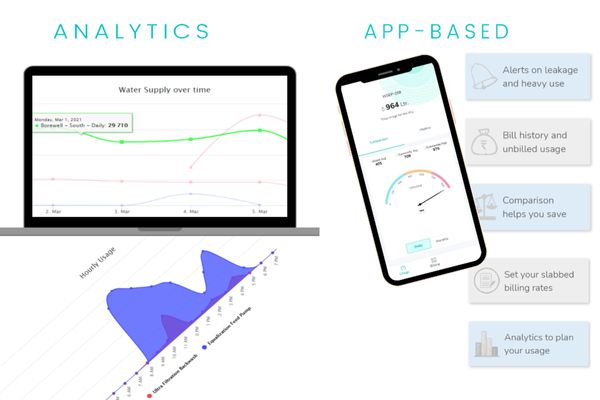
Smart Water Meters use transit time principle to measure water and provide real time information on usage and leaks without any hassle of manually reading the meters.

2025-10-15

2025-09-24